
How Is the Schedule Performance Index Calculated?Ĭalculated with the same input values as the schedule variance, namely: The SPI can be calculated for a particular period but also cumulative for all a number of periods of a project or the entire project. It measures the progress of a project compared to the planned schedule. The schedule performance index, too, belongs to the variance analysis techniques. What Is the Schedule Performance Index (SPI)? in the context of re-estimation ofĮxample of a Cost and Schedule Variance Analysis Diagram.

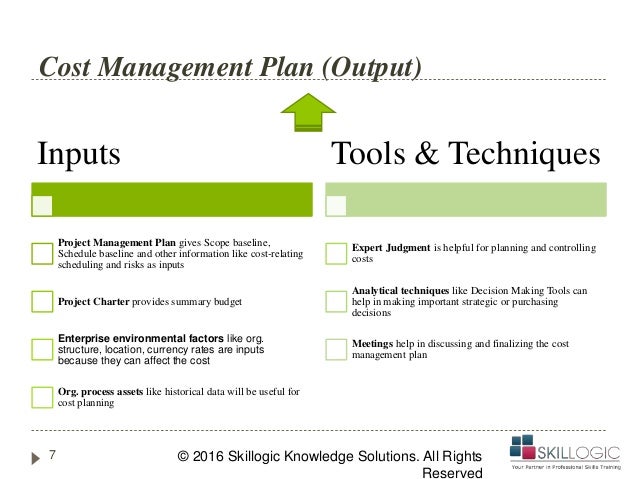
The CPI is also used to project cost incurrence for Variance, its result indicates the relative scale of deviations which helpsĪsses their criticality. Being calculated as a ratio rather than an absolute Performance index requires the input parametersĬPI = EV / AC How Is the CPI Interpreted? How Is the Cost Performance Index Calculated?Īs the cost variance calculation, the cost The CPI is used to compareĬosts and earned value at a point of time or cumulated over several periods ofĪ project. Part of the “control cost” process of a project. Of the variance analysis techniques which are, according to PMI methodology, The cost performance index is a component What Is the Cost Performance Index (CPI)? Formula for Cost Variance Calculationĭifference between earned value and actual cost:Ī negative amount indicates that the cost incurred to achieve the amount of work performed was higher than planned / budgeted.Įxamples of Cost Variance and Schedule Variance in a Diagram. It can also be used to calculate a forecast of the development of cost and future budget implications of a project. It compares the actual costs with the earned value. The cost variance is part of the variance analysis techniques. Variance Analysis for Cost and Schedule What Is the Cost Variance (CV)? ForĪccurate and meaningful results, it is important to define a single cost baseįor the budget and the actual cost (e.g. Work that has not been considered for the budget cannot be included). Actual Cost (AC)Īctual cost is the amount of cost that hasīeen realized for the authorized work performed (hence, cost for additional additionally performed work that has not been authorized and planned in the planned value cannot be accounted for in the earned value calculation. By definition, it cannot exceed the planned value, i.e. It relates to the part of the budget allocated to work that has been performed and completed. Earned Value (EV)Įarned value measures the materialized progress of a project. It is usually determined by estimatingĪctivities or elements of the Work Breakdown Structure. (before management reserve) that has been allocated to a project or a part of a The term planned value refers to the budget These indicators are often calculated in monetary The measures discussed in this articles are set out in the Earned Value Analysis (EVA) technique, introduced in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (source: PMBOK®, 6 th ed., ch. Project Cost Management is a key element of the Project Management methodology defined by the Project Management Institute.
Example 1: A Simple Calculation of Cost and Schedule.Examples Calculation and Use of CV, SV, CPI and SPI.How Is the Schedule Performance Index Calculated?.What Is the Schedule Performance Index (SPI)?.
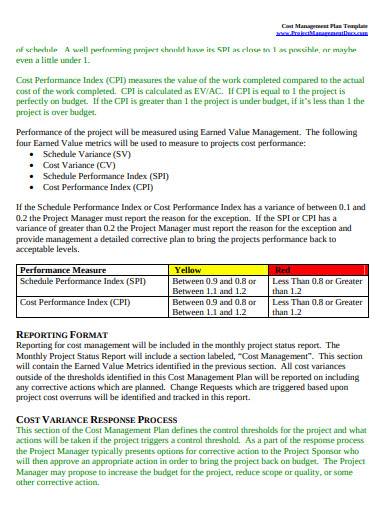
How Is the Cost Performance Index Calculated?.What Is the Cost Performance Index (CPI)?.Formula for Schedule Variance Calculation.Variance Analysis for Cost and Schedule.Fundamentals of Project Cost Measurements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
